Notes, musings and what not
Finding bugs with Syzkaller
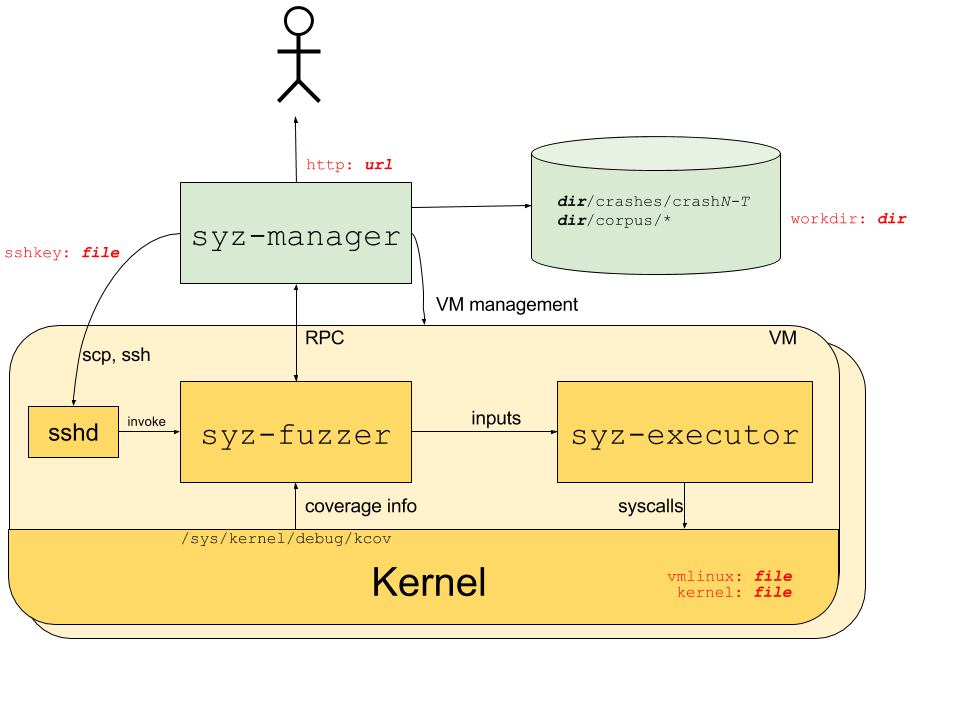
Syzkaller is an unsupervised, grammar based, coverage guided fuzzer used for fuzzing operating system kernels. It primarily performs system call fuzzing, but it can also be used for fuzzing USB and network packets. It is currently used for continuous fuzzing of Linux, Android and other BSD kernels.
- Automated: Syzkaller can automatically restart crashed virtual machines and also create a reproducer for the crashes.
- Coverage guided: Syzkaller gets coverage information using the KCOV infrastructure, which is built into the kernel. After executing a mutated program from the corpus, Syzkaller checks if the program has increased the coverage, i.e. it checks whether any new code paths in the kernel have been reached during the execution of the program. If so, it adds the program to the corpus for further mutation.
- Grammar based: Syzkaller understands the structure and API of system calls. It uses system calls descriptions written in Syzlang to generate valid system calls with randomized values in arguments. This allows it to execute deeper code paths that would not be possible with blind random fuzzing. Syzlang can describe structs that are passed as arguments to syscalls, the possible values for flags and resources (like file descriptors) which are passed across multiple syscalls and have to be created and destroyed using specific system calls.
Syzkaller overview
How to do research?
Disclaimer: I’m no expert in this. This post is just to collect all my thoughts and lessons learnt from random talks and blogs, about research.
What is research?
Research is producing new knowledge. The aim of research is to do something novel (new) and useful. The purpose of literature survey is to ensure that our idea is new and has not been proposed before. And the purpose of evaluations is to show that our idea or technique is useful.
…Kernel Sanitizers
When fuzzing a program by feeding random inputs to it, we need a mechanism to tell when the program is doing unexpected things. Sanitizers help detect bugs in the program at runtime. They are usually used along with fuzzing to detect bugs in programs.
The two roles of sanitizers:
- Detect incorrect program behaviour: like accessing memory that the program is not supposed to access
- Report incorrect behaviour: To be useful, the sanitizer needs to report useful information (like the stack trace and ) that makes it easier to understand and fix the bug.
The Linux kernel supports a number of sanitizers, each focussing on a different class of bugs.
…Linux kernel fuzzing
In this post, we’ll see how fuzzing is used for finding different types of bugs in the Linux kernel. This post consists of my notes taken from the talk by Andrey Konavalov about Linux fuzzing.
Operating systems kernels are complex. Testing kernels is of prime importance since any vulnerability in the kernel can lead to compromising the whole system.
Fuzzing is a dynamic program analysis technique, used to find bugs in software. It works by feeding random input to programs until it crashes. In recent times, Fuzzing has been effective in finding bugs, especially the ones that are hard to detect manually.
…TLB;DR Reversing TLBs with TLB desynchronization
Yesterday, I read an interesting research paper about reverse engineering TLBs using TLB desynchronization. In this post, I’ll write briefly about the key ideas and what I found very interesting in the paper.
You can find the paper here:
Reverse engineering CPU internals
In the subfield of hardware security that focuses on communicating (covert channels) or leaking (side channels) critical information using timing or storage channels, accurate information about the CPU internals helps create more efficient and reliable channels. Information about the size, associativity, set mapping, etc. of caches and TLBs allow the attacker to fine tune their attacks. However, most CPU vendors don’t disclose such information in detail, and so, attackers resort to reverse engineering these microarchitectural details. Reverse engineering hardware structures is usually performed by observing timing differences, which can have a lot of noise. In the paper, TLB;DR, the authors propose a new method for reverse engineering TLBs with high accuracy.
…